신생아 황달(신생아 빌리루빈 과잉혈/신생아 빌리루빈 과잉혈증/신생아 과빌리루빈 혈증/신생아 고빌리루빈 혈증), Neonatal jaundice (Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia)
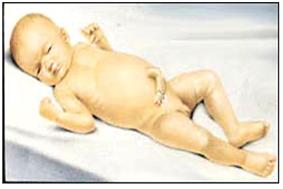
그림 117. 심한 신생아 황달
출처: Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA와 소아가정간호백과
- 신생아에게 생기는 황달을 통틀어 신생아 황달이라 하고 신생아 빌리루빈 과잉혈, 신생아 빌리루빈 과잉혈증, 신생아 고빌리루빈 혈증 또는 신생아 과빌리루빈 혈증이라고도 한다.
- 빌리루빈의 혈중 농도가 정상 이상으로 증가되어 피부와 눈 흰자위 등이 노랗게 될 수 있다.
- 황달은 어떤 병의 증상 징후이지 병명은 아니다.
- 정상 신생아들의 60%가 생후 7일 이내 황달에 걸린다.
- 혈액 내 적혈구에서 나온 빌리루빈은 간에서 UGTIAI 효소에 의해 빌리루빈 글루쿠론니드로 대사 된다.
- 빌리루빈은 담즙 성분의 일종이다.
- 혈액 내 적혈구에서 나온 빌리베리딘(Biliverdin)은 간에서 빌리루빈(Bilirubin)으로 전환된다. 빌리베리딘(Biliverdin)과 빌리루빈(Bilirubin)은 그때그때 적절히 담즙의 성분이 된다.
- 빌리루빈은 간접 빌리루빈(비포화 빌리루빈/간접형 빌리루빈/Unconjugate bilirubin/Indirect bilirubin)과 직접 빌리루빈(포화 빌리루빈/직접형 빌리루빈/Conjugate bilirubin/Direct bilirubin)이 있다. 빌리루빈은 담집의 성분이 되고 그 담집은 담관 속을 통해 십이지장관 속으로 분비된다.
- 생리적으로 또는 병적으로 혈 중 간접형 빌리루빈(Unconjugate bilirubin)을 정상 농도 이상이 되면 고빌리루빈혈증이 생기고 눈의 공막이 노랗고 피부가 노랗고 신생아 황달이 생긴다.
- 미국 만삭 신생아들과 거의 만삭에 가깝게 출생한 미숙아들의 1,000명 중 5~40명이 빌리루빈 광선요법으로 치료를 받는다(출처; NEJM Febuary 2008 p.920).
- 신생아 황달의 원인, 증상 징후, 치료, 예후 등이 신생아기 이후의 영유아들이나 학령기 아이들이나 성인들에게 생기는 황달의 원인, 증상 징후, 치료, 예후기와 다른 점이 많다.
| 신생아 황달과 신생아기 이후 황달의 분류 |
- 모유와 신생아 황달
- 용혈성 빈혈
- 미숙 신생아 황달
- 생리적 신생아 황달
- Rh 부적합으로 인한 신생아 황달
- ABO 혈액형 부적합으로 인한 신생아 황달
- 모유를 먹는 신생아에게 생기는 신생아 황달
- 간염으로 인한 신생아 황달
- 선천성 담관 폐쇄로 생기는 신생아 황달
- G-6-인산 포도당 탈수소효소 결핍(G-6-P-D 결핍)으로 인한 신생아 황달
- 다른 원인으로 인한 신생아 황달
표 2. 신생아 과빌리루빈 혈증
| 빌리루빈 생성이 증가될 때 | 빌리루빈 분비가 감소될 때 | 빌리루빈 생성이 증가되고 빌리루빈 분비가 감소될 때 |
|
·ABO 혈액형 부적합으로 생기는 신생아 황달 ·G-6-PD 결핍(G-6-PD deficiency)으로 인한 신생아 황달 |
·생리적 신생아 황달 ·모유수유 황달 ·장관폐쇄 ·임신부 간질환 ·유전성 빌리루빈 분비장애 ·크리글러 나잘 증후군(크리글러-나자르증후군) Crigler-Najjar syndrome, 1형과 2형 ·루시 드리시클 증후군(Lucey Driscoll syndrome) |
·미숙아 ·패혈증 |
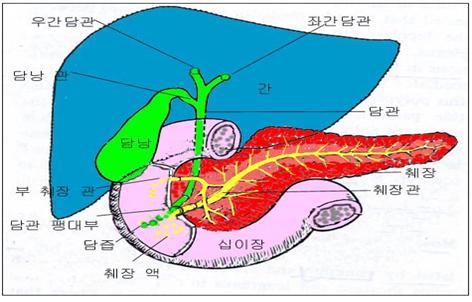
그림 118.간, 췌장과 담즙 분비관, 십이지장관
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
Neonatal jaundice (Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia)

Figure 117. Severe Neonatal Jaundice Source: Ross Laboratories, Columbus, Ohio 43216, Division of Laboratories, USA and Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing
• Jaundice that occurs in newborns is collectively called neonatal jaundice and is also called neonatal hyperbilirubinemia.
• Blood levels of bilirubin increase above normal, which may cause the skin and whites of the eyes to turn yellow.
• Jaundice is a symptom of a disease, not a name of disease.
• 60% of normal newborns develop jaundice within the first 7 days of life.
• Bilirubin from red blood cells in the blood is metabolized to bilirubin glucuronide by the UGTIAI enzyme in the liver.
• Bilirubin is a type of bile component.
• Biliverdin from red blood cells in the blood is converted to bilirubin in the liver.
Biliverdin and bilirubin are appropriate components of bile from time to time.
• Bilirubin includes indirect bilirubin (unsaturated bilirubin/indirect bilirubin/unconjugated bilirubin/indirect bilirubin) and direct bilirubin (saturated bilirubin/direct bilirubin/conjugate bilirubin).
Bilirubin becomes a component of the bile, and the bile is secreted into the duodenum.
• When unconjugated bilirubin in the blood exceeds normal levels physiologically or pathologically, hyperbilirubinemia occurs, the sclera of the eye is yellow, the skin is yellow, and neonatal jaundice occurs.
• In the United States, 5 to 40 out of 1,000 full-term newborns and near-term premature babies are treated with bilirubin phototherapy (source; NEJM Febuary 2008 p.920).
• The causes, symptoms, signs, treatment, and prognosis of neonatal jaundice are different from the causes, symptom, signs, treatment, and prognosis of jaundice in infants and children after the neonatal period, school-age children and adults.
Classification of neonatal jaundice and post-neonatal jaundice
1. Breast milk and neonatal jaundice
2. Hemolytic anemia
3. Jaundice in premature newborns
4. Physiological neonatal jaundice
5. Neonatal jaundice due to Rh incompatibility
6. Neonatal jaundice due to ABO blood group incompatibility
7. Neonatal jaundice in breastfed newborns
8. Neonatal jaundice due to hepatitis
9. Neonatal jaundice due to congenital bile duct obstruction
10. Neonatal jaundice due to G-6-phosphate glucose dehydrogenase deficiency (G-6-P-D deficiency)
11. Newborn Jaundice from Other Causes
Table 2. Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia
표 2. 신생아 과빌리루빈 혈증
| When bilirubin production is increased | When bilirubin secretion is decreased | When bilirubin production is increased and bilirubin secretion is decreased |
|
|
|

Figure 118. Liver, pancreas and biliary tract, duodenum.
Copyright ⓒ 2012 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
출처와 참조문헌
- Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
-
소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
-
Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
-
Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
-
Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- Growth and Development of Children, Eighth Edition, George H. Lowrey, Yearbook Medical Publishers
- Growth and Development of Children, Fifth Edition, E. H. Watson and G. H. Lowrey, Yearbook Medical Publishers
- Other